News
Microsoft Talks Up Windows Server 'Shielded VMs'
- By Kurt Mackie
- May 13, 2016
Microsoft recently put the spotlight on Shielded Virtual Machines (VMs), its datacenter security technology aimed at protecting workloads in public and private datacenters from "malicious administrators."
Shielded VMs, which Microsoft describes as an attestation scheme that gives greater control to tenant administrators, can be enabled for Windows Server 2016 tenants, as well as those using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2. Right now, it only works with Gen-2 VMs. It's possible to convert existing Gen-2 VMs to Shielded VMs.
It turns out that a VM "is just a file," and it can be run on any other system if it gets copied out of an organization, according to Microsoft's TechNet "Overview" article. A VM can be copied by any administrator that has access to the tenant, such as a storage admin or a backup admin. Microsoft's Shielded VM scheme uses BitLocker encryption to block access to the VM file to all but the tenant administrator.
A rogue administrator could copy a VM onto a memory stick and later try to break it, this Microsoft Mechanics video explained. It might take four or five days to extract the information using hacking tools, said Dean Wells, a principal program manager lead for Windows Server and Services, in the video.
To prevent such security breaches, a Shielded VM can get created using the Windows Azure Pack, which is a bunch of datacenter tools that Microsoft first released for Windows Server 2012 R2. The option to create a Shielded VM shows up in the Azure Pack UI with a shield icon on it.
Shielded VMs are based on Microsoft's Guarded Fabric technology, which "enforces strong isolation boundaries between the host and its own VM," Wells explained, which means that the host can't get at the VM's data.
The Guarded Fabric has four component parts, according to Wells. Its Code Integrity component measures code integrity polices on the machine and all of the things that loaded on boot-up to ensure they are healthy. It has a Virtual Security Mode that cordons off memory so that admins can't get to it. The Virtual Security Mode has so-called "trustlets" that keep the key encrypted and away from malicious admins. The third component is Trusted Platform Module V2. It's a virtual Trusted Platform Module that enables secure measured boot, but it's not related to the physical TPM on the Hyper-V host. The last component of the Guarded Fabric is the Host Guardian Service, which runs on a cluster and adds security-key protection and attestation services (see figure).
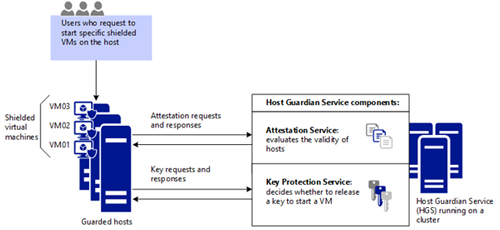 [Click on image for larger view.] Host Guardian Service component. (Source: Microsoft TechNet article.)
[Click on image for larger view.] Host Guardian Service component. (Source: Microsoft TechNet article.)
Surprisingly, Shielded VMs are a bit more advanced on the Windows Server side right now. Microsoft Azure doesn't support them yet, Wells said.
It's possible to test the Shielded VM technology with Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 4, which was released in November. Microsoft is targeting commercial release of Windows Server 2016 in Q3 of this year.
About the Author
Kurt Mackie is senior news producer for 1105 Media's Converge360 group.